The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag.
Example is shown below:
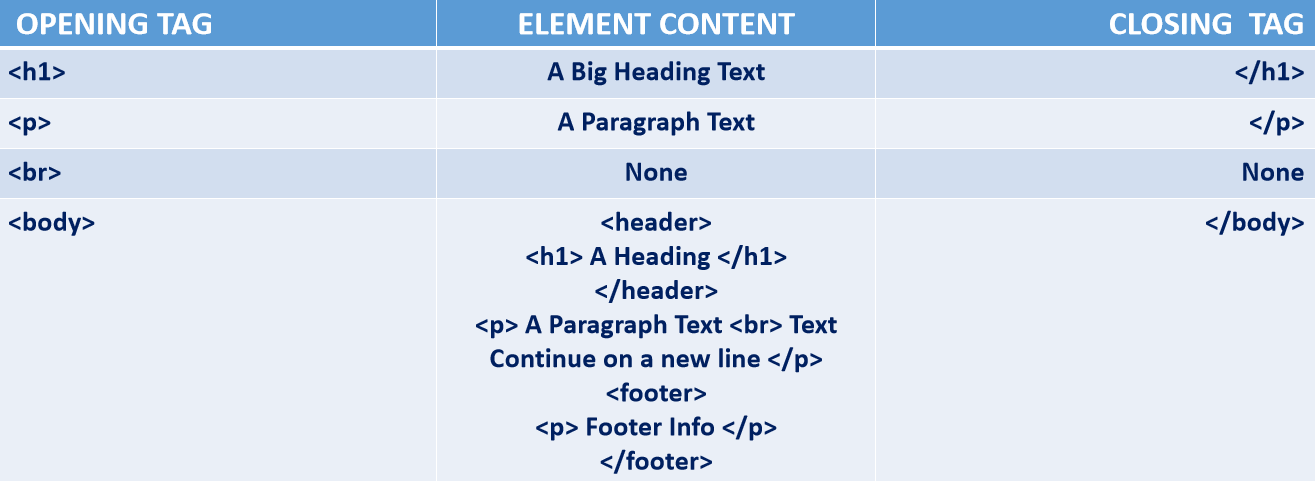
Note:
* HTML elements with no content are called empty elements.
Empty elements do not have an end tag, such as the element (which indicates a line break).
* There also elements known as the self closing elements.
These type of element open and close within themselves,
their opening and closing tags are combined in one.
An example of such element is the Image (img) element.
E.g <img src="" alt=""/>
The contents of this type of tag is written within the same opening tag followed by a backwards slash.
some examples of such tags are:
And so On...
HTML <html> Tag
The <html> ag tells the browser that this is an HTML document.
The <html> tag represents the root of an HTML document.
The <html> tag is the container for all other HTML elements (except for the <!DOCTYPE> tag)
The main child-elements of the <html> tag are the head and body elememts, written within the following tags:
HTML head Tag
The <head> element is a container for all the head elements.
The <head> element can include a title for the document, scripts, styles, meta information, and more.
The following elements can go inside the <head> element:
HTML body Tag
The <body> tag defines the document's body..
The <body> element contains all the contents of an HTML document, such as text, hyperlinks, images, tables, lists, etc.
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
</head>
<body>
The content of the document......
</body>
</html>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
Note:
1. The Head and Body Elements are contained inside the html Element.
2. The Head Element contains all the meta element, links, internal CSS style, and the title element,
3. While the body element contains every other html elements apart from the ones contained be the head element.
4. Only codes written within the body element are displayed by the browser.
5. Be Reminded that, An Element is comprised of both the opening tag and the closing tag, with the contents inbetween both tags.
HTML Headings
<h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading:
<h1> This is Heading 1 </h1>
<h2> This is Heading 2 </h2>
<h3> This is Heading 3 </h3>
<h4> This is Heading 4 </h4>
<h5> This is Heading 5 </h5>
<h6> This is Heading 6 </h6>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
HTML Paragraphs
<p> This is a Paragraph </p>
<p> This is another paragraph </p>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
HTML Anchor Link Tag
<a href="https://google.com"> This is a Link </a>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
The link's destination is specified in the href attribute.
Attributes are used to provide additional information about HTML elements.
You will learn more about attributes in a later section.
HTML Images
<img src="w3schools.jpg" alt="W3Schools.com" width="104" height="142"/>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
The source file ( src ), alternative text ( alt ), width, and height are provided as attributes:
HTML Buttons
<button> Click Me </button>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
HTML Lists
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
<li>Item 4</li>
</ul>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
<ol>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
<li>Item 4</li>
</ol>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
HTML Strong Tag
<p> This is normal text - <strong> and this is bold text</strong> </p>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
<p> This is normal text - <b> and this is bold text</b> </p>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
HTML Emphasize Tag
<p> This is normal text - <em> and this is italic text</em> </p>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output
<p> This is normal text - <i> and this is italic text</i> </p>
NOTE : Copy and run the code to see the output